Differences
This shows you the differences between two versions of the page.
| Both sides previous revisionPrevious revisionNext revision | Previous revisionNext revisionBoth sides next revision | ||
| teaching:gsoc2014 [2014/02/25 13:31] – [Topic 2: CRAM -- Symbolic Reasoning Tools with Bullet] tenorth | teaching:gsoc2014 [2014/03/06 11:42] – [Google Summer of Code 2014] tenorth | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{ : | ||
| ====== Google Summer of Code 2014 ====== | ====== Google Summer of Code 2014 ====== | ||
| ~~NOTOC~~ | ~~NOTOC~~ | ||
| Line 8: | Line 9: | ||
| are available under BSD license, and partly (L)GPL. | are available under BSD license, and partly (L)GPL. | ||
| + | If you are interested in working on a topic and meet its general criteria, you should have a look at the [[teaching: | ||
| ===== KnowRob -- Robot Knowledge Processing ===== | ===== KnowRob -- Robot Knowledge Processing ===== | ||
| Line 50: | Line 52: | ||
| human robot interaction (SAPHARI). | human robot interaction (SAPHARI). | ||
| Further information, | Further information, | ||
| - | use-cases can be found at the [[http:// | + | use-cases can be found at the [[http:// |
| website]]. | website]]. | ||
| Line 57: | Line 59: | ||
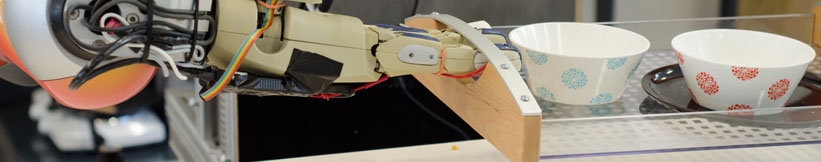
| ==== CRAM -- Virtual Robot Scenarios in Gazebo ==== | ==== CRAM -- Virtual Robot Scenarios in Gazebo ==== | ||
| + | {{ : | ||
| **Main Objective: | **Main Objective: | ||
| for human-sized robots. This is done using ROS, the Gazebo robot | for human-sized robots. This is done using ROS, the Gazebo robot | ||
| Line 64: | Line 67: | ||
| and closing drawers and doors. | and closing drawers and doors. | ||
| This involves designing virtual environments for Gazebo and/or writing robot plans in Lisp using the CRAM high-level language, sending commands to virtual PR2 or REEM(-C) robots in Gazebo, and manipulating the artificial environment in there. The connection to an elaborate high-level system holds a lot of interesting opportunities. | This involves designing virtual environments for Gazebo and/or writing robot plans in Lisp using the CRAM high-level language, sending commands to virtual PR2 or REEM(-C) robots in Gazebo, and manipulating the artificial environment in there. The connection to an elaborate high-level system holds a lot of interesting opportunities. | ||
| + | {{ : | ||
| The produced code will, when working in a simulated environment, | The produced code will, when working in a simulated environment, | ||
| Line 72: | Line 76: | ||
| robot' | robot' | ||
| - | ==== Topic 2: CRAM -- Symbolic Reasoning Tools with Bullet ==== | + | Contact: [[team/ |
| - | **Main Objective: | + | ==== Topic 2: CRAM -- Symbolic Reasoning Tools with Bullet ==== |
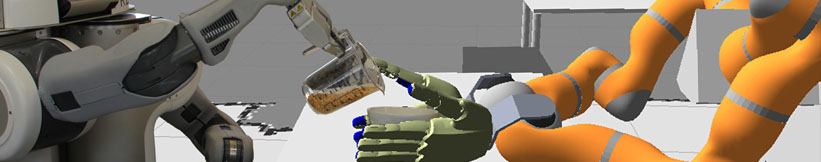
| + | {{ : | ||
| + | **Main Objective: **Mapping the environment to the internal belief state representation and keeping track of changes in the environment to keep the belief state up to date based on manipulation and interaction tasks performed by the robot.\\ | ||
| **Task Difficulty: | **Task Difficulty: | ||
| + | {{ : | ||
| **Requirements: | **Requirements: | ||
| - | **Expected Results:** We expect operational and robust contributions to the software library that can be used as part of a robot' | + | **Expected Results:** We expect operational and robust contributions to the software library that can be used as a part of robot' |
| + | Contact: [[team/ | ||
| + | ==== Topic 3: KnowRob -- Reasoning about 3D CAD models of objects ==== | ||
| + | < | ||
| + | **Main Objective: | ||
| + | need information about their geometry. While the overall shape is | ||
| + | sufficient for picking up an object, more information about its | ||
| + | composition from parts and their meaning (e.g. a handle or a container) | ||
| + | is needed when using objects as tools in more complex activities. | ||
| + | We have developed an initial version of a program library that is able | ||
| + | to analyze CAD models of objects, as they can be found in large databases | ||
| + | on the Web, and to automatically identify such functional components. | ||
| + | As part of this project, that software library is to be extended in | ||
| + | order to recognized additional geometric primitives (e.g. torus, box) | ||
| + | and to improve the segmentation and make it more robust. Alternatively, | ||
| + | the focus could be more on improving the analysis infrastructure and | ||
| + | integrating it more closely with the robot' | ||
| + | **Task Difficulty: | ||
| + | ranges from rather simple tasks at the infrastructure level to | ||
| + | interesting research problems for the geometric analysis.\\ | ||
| + | **Requirements: | ||
| + | solid understanding of 3D geometry. Good programming skills in Java | ||
| + | are needed for implementing the algorithms and for evaluating their | ||
| + | results. Depending on the exact topic, knowledge of machine learning | ||
| + | methods or the ability to learn about them could be helpful.\\ | ||
| + | **Expected Results:** We expect operational and robust contributions | ||
| + | to the software library that can be used as part of a robot' | ||
| + | program. | ||
| + | Contact: [[team/ | ||
Prof. Dr. hc. Michael Beetz PhD
Head of Institute
Contact via
Andrea Cowley
assistant to Prof. Beetz
ai-office@cs.uni-bremen.de
Discover our VRB for innovative and interactive research

Memberships and associations: