Differences
This shows you the differences between two versions of the page.
| Both sides previous revisionPrevious revisionNext revision | Previous revision | ||
| team:feroz_ahmed_siddiky [2022/07/14 11:08] – siddiky | team:feroz_ahmed_siddiky [2024/06/05 10:31] (current) – [Feroz Ahmed Siddiky] cstoess | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
| | {{: | | {{: | ||
| |::: ||Research Staff\\ \\ || | |::: ||Research Staff\\ \\ || | ||
| - | |:::|Tel: |–49 -421 218 64027| | + | |:::|Tel: |–49 -421 218 64028| |
| |:::|Fax: |--49 -421 218 64047| | |:::|Fax: |--49 -421 218 64047| | ||
| |:::|Room: |TAB 1.81| | |:::|Room: |TAB 1.81| | ||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
| |:::| || | |:::| || | ||
| - | ====Projects involved in===== | + | ==== Deep Action Obserever |
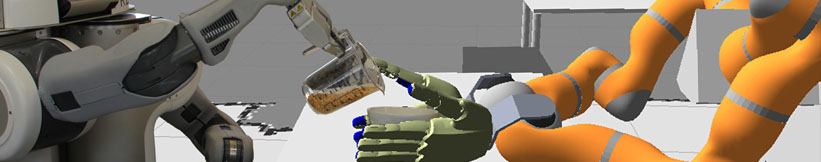
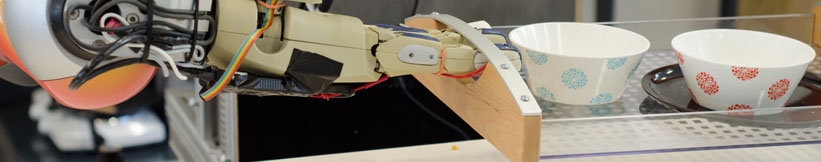
| - | * [[http:// | + | Robotic agents have to learn how to perform manipulation tasks. One of the biggest challenges in this context is that |
| - | * [[https:// | + | manipulation actions are performed in a variety of ways depending on the objects that the robot acts on, the tools it is |
| - | * [[http:// | + | using, the task context, as well as the scene the action is to be executed in. This raises the issue of when to perform |
| - | * [[http://www.robohow.org|RoboHow]] | + | a manipulation action in which way. In this paper we propose to let the robot read text instructions and watch the |
| + | corresponding videos illustrating how the steps are performed in order to generate symbolic action descriptions from the | ||
| + | text instructions. The text instructions are disambiguated and completed with the information contained in the videos. The | ||
| + | resulting action descriptions are close to action descriptions that can be executed by leading-edge cognition-enabled robot | ||
| + | control plans. To perform this learning task we combine two of the most powerful learning and reasoning mechanisms: | ||
| + | Deep Learning and Markov Logic Networks. Convolutional networks parameterized through deep learning recognize | ||
| + | objects, hand poses, and estimate poses and motions while the Markov logic networks use joint probability over the | ||
| + | relational structure of instructions to fill in missing information and disambiguate descriptions. Besides the combination | ||
| + | of symbolic and sub-symbolic reasoning the novel contributions include a Multi Task Network developed in a single | ||
| + | framework, optimized for computational cost, which can process 10 frames per second. We evaluate our framework on a | ||
| + | large number of video clips and show its impressive ability to interpret the manipulation tasks. | ||
| + | [1] Feroz Ahmed Siddiky and Michael Beetz, " | ||
Prof. Dr. hc. Michael Beetz PhD
Head of Institute
Contact via
Andrea Cowley
assistant to Prof. Beetz
ai-office@cs.uni-bremen.de
Discover our VRB for innovative and interactive research

Memberships and associations: