Differences
This shows you the differences between two versions of the page.
| Both sides previous revisionPrevious revisionNext revision | Previous revisionNext revisionBoth sides next revision | ||
| teaching:gsoc2018 [2018/01/21 20:29] – balintbe | teaching:gsoc2018 [2018/01/22 09:36] – [openEASE -- Web-based Robot Knowledge Service] ahaidu | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
| RoboSherlock builds on top of the ROS ecosystem and is able to wrap almost any existing perception algorithm/ | RoboSherlock builds on top of the ROS ecosystem and is able to wrap almost any existing perception algorithm/ | ||
| + | ===== openEASE -- Web-based Robot Knowledge Service ===== | ||
| + | OpenEASE is a generic knowledge database for collecting and analyzing experiment data. Its foundation is the KnowRob knowledge processing system and ROS, enhanced by reasoning mechanisms and a web interface developed for inspecting comprehensive experiment logs. These logs can be recorded for example from complex CRAM plan executions, virtual reality experiments, | ||
| + | |||
| + | The OpenEASE web interface as well as further information and publication material can be accessed through its publicly available [[http:// | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== RobCoG - **Rob**ot **Co**mmonsense **G**ames ===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[http:// | ||
| ===== Proposed Topics ===== | ===== Proposed Topics ===== | ||
| Line 76: | Line 84: | ||
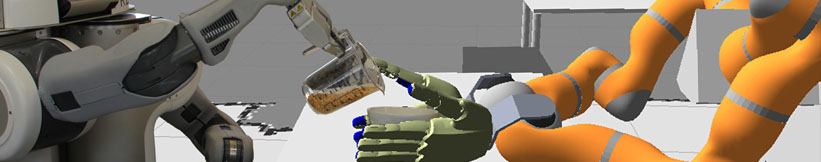
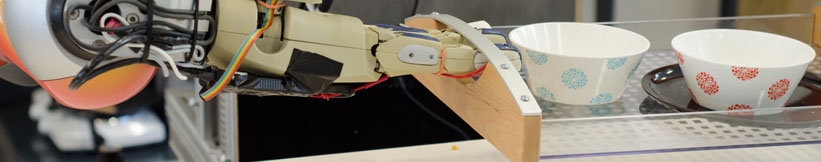
| - | ==== Topic 1: Multi-modal Cluttered Scene Analysis in Knowledge Intensive Scenarios | + | ==== Topic 2: Felxible perception pipeline manipulation for RoboSherlock |
| {{ : | {{ : | ||
| - | **Main Objective: | + | **Main Objective: |
| - | able robots | + | |
| - | cult and challenging scenarios. To achieve this the participant will | + | |
| - | develop annotators | + | |
| - | object-hypotheses generation | + | |
| - | essentially means to generate regions/ | + | |
| - | form a single object or object-part. In particular this entails the de- | + | |
| - | velopment of segmentation algorithms for visually challenging scenes | + | |
| - | or object properties, as the likes of transparent objects, or cluttered, | + | |
| - | occluded scenes. The addressed scenarios include stacked, occluded | + | |
| - | objects placed on shelves, objects | + | |
| - | ers, cupboards etc. In typical scenarios, these confined spaces also | + | |
| - | bare an underlying structure, which will be exploited, and used as | + | |
| - | background knowledge, to aid perception (e.g. stacked plates would | + | |
| - | show up as parallel lines using an edge detection). Specifically we | + | |
| - | would start from (but not necessarly limit ourselves to) the implemen- | + | |
| - | tation | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | [1] Aleksandrs Ecins, Cornelia Fermuller and Yiannis Aloimonos, Cluttered Scene Segmentation Using the Symmetry Constraint, International Conference on Robotics and Automation(ICRA) 2016 | + | |
| - | [2] Richtsfeld A., M ̈ | + | |
| - | orwald T., Prankl J., Zillich M. and Vincze | + | |
| - | M. - Segmentation of Unknown Objects in Indoor Environments. | + | |
| - | IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Sys- | + | |
| - | tems (IROS), 2012. | + | |
| - | **Task Difficulty: | + | **Task Difficulty: |
| | | ||
| **Requirements: | **Requirements: | ||
| - | **Expected Results: | + | **Expected Results: |
| Contact: [[team/ | Contact: [[team/ | ||
Prof. Dr. hc. Michael Beetz PhD
Head of Institute
Contact via
Andrea Cowley
assistant to Prof. Beetz
ai-office@cs.uni-bremen.de
Discover our VRB for innovative and interactive research

Memberships and associations: