Differences
This shows you the differences between two versions of the page.
| Both sides previous revisionPrevious revisionNext revision | Previous revisionNext revisionBoth sides next revision | ||
| teaching:gsoc2018 [2018/01/17 17:48] – [Topic 1: Markov logic networks in Python] nyga | teaching:gsoc2018 [2018/01/21 20:29] – balintbe | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
| package in the Python package index ([[https:// | package in the Python package index ([[https:// | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== RoboSherlock -- Framework for Cognitive Perception ===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | RoboSherlock is a common framework for cognitive perception, based on the principle of unstructured information management (UIM). UIM has proven itself to be a powerful paradigm for scaling intelligent information and question answering systems towards real-world complexity (i.e. the Watson system from IBM). Complexity in UIM is handled by identifying (or hypothesizing) pieces of | ||
| + | structured information in unstructured documents, by applying ensembles of experts for annotating information pieces, and by testing and integrating these isolated annotations into a comprehensive interpretation of the document. | ||
| + | |||
| + | RoboSherlock builds on top of the ROS ecosystem and is able to wrap almost any existing perception algorithm/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Proposed Topics ===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the following, we list our proposals for the Google Summer of Code topics that contribute to the aforementioned open-source projects. | ||
| ==== Topic 1: Markov logic networks in Python ==== | ==== Topic 1: Markov logic networks in Python ==== | ||
| Line 62: | Line 74: | ||
| **Contact: | **Contact: | ||
| - | ===== Proposed Topics ===== | ||
| - | In the following, | + | |
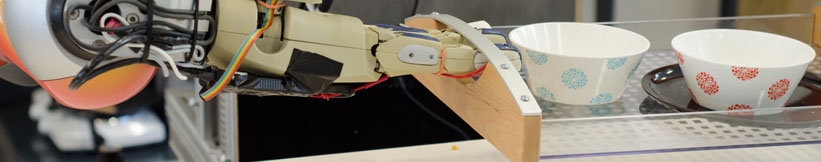
| + | ==== Topic 1: Multi-modal Cluttered Scene Analysis in Knowledge Intensive Scenarios ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{ : | ||
| + | |||
| + | **Main Objective: | ||
| + | able robots in a human environment to recognize objects in diffi- | ||
| + | cult and challenging scenarios. To achieve this the participant will | ||
| + | develop annotators for RoboSherlock that are particularly aimed at | ||
| + | object-hypotheses generation and merging. Generating a hypotheses | ||
| + | essentially means to generate regions/ | ||
| + | form a single object or object-part. In particular this entails the de- | ||
| + | velopment of segmentation algorithms | ||
| + | or object properties, as the likes of transparent objects, or cluttered, | ||
| + | occluded scenes. The addressed scenarios include stacked, occluded | ||
| + | objects placed on shelves, objects in drawers, refrigerators, | ||
| + | ers, cupboards etc. In typical scenarios, these confined spaces also | ||
| + | bare an underlying structure, which will be exploited, and used as | ||
| + | background knowledge, | ||
| + | show up as parallel lines using an edge detection). Specifically we | ||
| + | would start from (but not necessarly limit ourselves to) the implemen- | ||
| + | tation of two state-of-the-art algorithms described in recent papers: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [1] Aleksandrs Ecins, Cornelia Fermuller and Yiannis Aloimonos, Cluttered Scene Segmentation Using the Symmetry Constraint, International Conference on Robotics and Automation(ICRA) 2016 | ||
| + | [2] Richtsfeld A., M ̈ | ||
| + | orwald T., Prankl J., Zillich M. and Vincze | ||
| + | M. - Segmentation of Unknown Objects in Indoor Environments. | ||
| + | IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Sys- | ||
| + | tems (IROS), 2012. | ||
| + | |||
| + | **Task Difficulty: | ||
| + | |||
| + | **Requirements: | ||
| + | |||
| + | **Expected Results:** Currently the RoboSherlock framework lacks good perception algorithms that can generate object-hypotheses in challenging scenarios(clutter and/or occlusion). The expected results are several software components based on recent advances in cluttered scene analysis that are able to successfully recognized objects in the scenarios mentioned in the objectives, or a subset of these. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Contact: [[team/ | ||
| + | |||
Prof. Dr. hc. Michael Beetz PhD
Head of Institute
Contact via
Andrea Cowley
assistant to Prof. Beetz
ai-office@cs.uni-bremen.de
Discover our VRB for innovative and interactive research

Memberships and associations: