Differences
This shows you the differences between two versions of the page.
| Both sides previous revisionPrevious revisionNext revision | Previous revisionNext revisionBoth sides next revision | ||
| teaching:gsoc2017 [2017/02/08 08:08] – [CRAM -- Robot Plans] lisca | teaching:gsoc2017 [2017/02/08 08:11] – [Topic 1: Multi-modal Cluttered Scene Analysis in Knowledge Intensive Scenarios] lisca | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
| use-cases can be found at the [[http:// | use-cases can be found at the [[http:// | ||
| website]]. | website]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== openEASE -- Experiment Knowledge Database ===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | OpenEASE is a generic knowledge database for collecting and analysing experiment data. Its foundation is the KnowRob knowledge processing system and ROS, enhanced by reasoning mechanisms and a web interface developed for inspecting comprehensive experiment logs. These logs can be recorded for example from complex CRAM plan executions, virtual reality experiments, | ||
| + | |||
| + | The OpenEASE web interface as well as further information and publication material can be accessed through its publicly available [[http:// | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== RoboSherlock -- Framework for Cognitive Perception ===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | RoboSherlock is a common framework for cognitive perception, based on the principle of unstructured information management (UIM). UIM has proven itself to be a powerful paradigm for scaling intelligent information and question answering systems towards real-world complexity (i.e. the Watson system from IBM). Complexity in UIM is handled by identifying (or hypothesizing) pieces of | ||
| + | structured information in unstructured documents, by applying ensembles of experts for annotating information pieces, and by testing and integrating these isolated annotations into a comprehensive interpretation of the document. | ||
| + | |||
| + | RoboSherlock builds on top of the ROS ecosystem and is able to wrap almost any existing perception algorithm/ | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===== Proposed Topics ===== | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the following, we list our proposals for the Google Summer of Code topics that contribute to the aforementioned | ||
| + | open-source projects. | ||
| + | |||
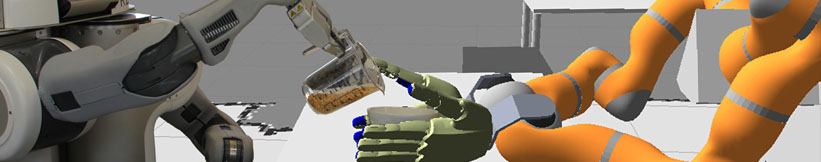
| + | ==== Topic 1: Multi-modal Cluttered Scene Analysis in Knowledge Intensive Scenarios ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{ : | ||
| + | |||
| + | **Main Objective: | ||
| + | edge detection). | ||
| + | |||
| + | **Task Difficulty: | ||
| + | | ||
| + | **Requirements: | ||
| + | |||
| + | **Expected Results:** Currently the RoboSherlock framework lacks good perception algorithms that can generate object-hypotheses in challenging scenarios(clutter and/or occlusion). The expected results are several software components based on recent advances in cluttered scene analysis that are able to successfully recognized objects in the scenarios mentioned in the objectives, or a subset of these. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Contact: [[team/ | ||
| + | |||
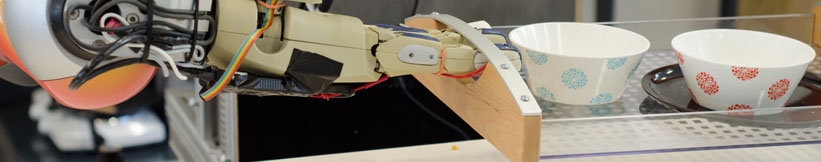
| + | ==== Topic 2: Realistic Grasping using Unreal Engine ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{ : | ||
| + | |||
| + | **Main Objective: | ||
| + | ious human-like grasping approaches in a game developed using [[https:// | ||
| + | |||
| + | The game consist of a household environment where a user has to execute various given tasks, such as cooking a dish, setting the table, cleaning the dishes etc. The interaction is done using various sensors to map the users hands onto the virtual hands in the game. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In order to improve the ease of manipulating objects the user should | ||
| + | be able to switch during runtime the type of grasp (pinch, power | ||
| + | grasp, precision grip etc.) he/she would like to use. | ||
| + | |||
| + | **Task Difficulty: | ||
| + | level, as it requires less algorithmic knowledge and more programming skills. | ||
| + | | ||
| + | **Requirements: | ||
| + | |||
| + | **Expected Results** We expect to enhance our currently developed robot learning game with realistic human-like grasping capabilities. These would allow users to interact more realistically with the given virtual environment. Having the possibility to manipulate objects of various shapes and sizes will allow to increase the repertoire of the executed tasks in the game. Being able to switch between specific grasps will allow us to learn grasping models specific to each manipulated object. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Contact: [[team/ | ||
Prof. Dr. hc. Michael Beetz PhD
Head of Institute
Contact via
Andrea Cowley
assistant to Prof. Beetz
ai-office@cs.uni-bremen.de
Discover our VRB for innovative and interactive research

Memberships and associations: