Differences
This shows you the differences between two versions of the page.
| Both sides previous revisionPrevious revisionNext revision | Previous revisionNext revisionBoth sides next revision | ||
| research:roboearth [2012/09/19 13:18] – pmania | research:roboearth [2012/09/28 07:59] – asil | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
| // | // | ||
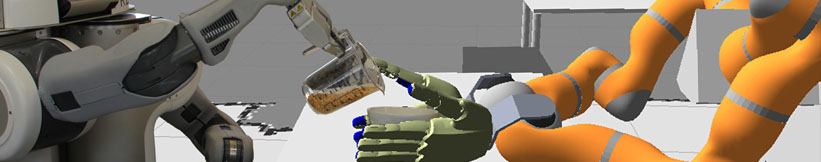
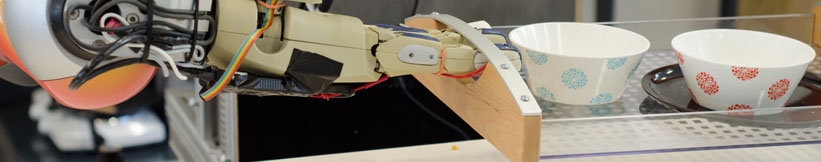
| - | The [[http:// | + | The [[http:// |
| {{ : | {{ : | ||
| + | These libraries of action recipes that are shared between robots will drastically reduce the efforts for building new robot applications. | ||
| - | The central | + | Within the RoboEarth |
| - | all of them have different requirements on capabilities a robot must have in | + | |
| - | order to use them. The developed language thus provides methods | + | |
| - | these required capabilities against those available on the robot. | + | |
| - | Each robot has a self-model consisting of a description of its kinematic | + | |
| - | structure, including the positions of sensors and actuators, a semantic | + | |
| - | model that describes the meaning of the robot' | + | |
| - | form a gripper), and a set of software components like object recognition | + | |
| - | systems. We developed the [[http:// | + | |
| - | More information can be found on the RoboEarth project homepage. | + | More information can be found on the [[http:// |
| [[http:// | [[http:// | ||
| + | |||
| + | Key publications within [[http:// | ||
| + | |||
| ==== Acknowledgements ==== | ==== Acknowledgements ==== | ||
| This project has received funding from the European Union Seventh Framework Programme FP7/ | This project has received funding from the European Union Seventh Framework Programme FP7/ | ||
| - | |||
| - | === Publications === | ||
Prof. Dr. hc. Michael Beetz PhD
Head of Institute
Contact via
Andrea Cowley
assistant to Prof. Beetz
ai-office@cs.uni-bremen.de
Discover our VRB for innovative and interactive research

Memberships and associations: