Differences
This shows you the differences between two versions of the page.
| Next revision | Previous revisionNext revisionBoth sides next revision | ||
| research:roboearth [2012/09/19 13:18] – created pmania | research:roboearth [2014/02/18 14:35] – yfang | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | ====== RoboEarth: Knowledge-exchange between robots ====== | + | ===== RoboEarth: |
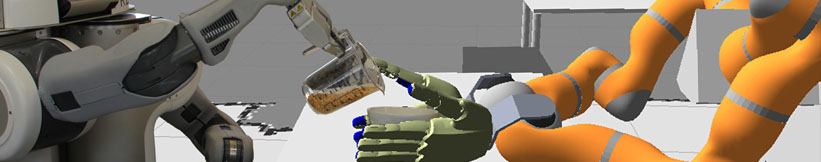
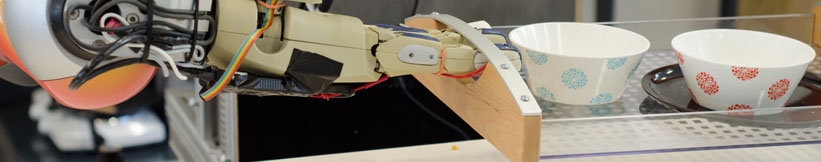
| + | The purpose of the RoboEarth project is to create a giant network through which robots and their programmers can easily share information about actions and the world. Similar to what the World Wide Web has done for humans, RoboEarth will enable robotic systems to benefit from the experience of other robots in a way that can be easily translated to their own case. Data stored in RoboEarth include software components, environment maps, task knowledge, and object recognition models. The network will provide a key infrastructure for advancing machine cognition and behavior incrementally on a collective level. In addition the RoboEarth Cloud Engine will make powerful computation available to robots. | ||
| - | The [[http:// | + | Our role in the RoboEarth consortium is to investigate knowledge representation and mechanisms for uploading, exchanging and applying action recipes. For this purpose we build upon our Cognitive Robot Abstract Machine ([[:research: |
| - | {{ : | + | < |
| - | The central RoboEarth knowledge base contains descriptions of actions (called " | + | For more information and news, visit www.roboearth.org |
| - | all of them have different requirements on capabilities a robot must have in | + | |
| - | order to use them. The developed language thus provides methods for matching | + | |
| - | these required capabilities against those available on the robot. | + | |
| - | Each robot has a self-model consisting of a description of its kinematic | + | |
| - | structure, including the positions of sensors and actuators, a semantic | + | |
| - | model that describes the meaning of the robot' | + | |
| - | form a gripper), and a set of software components like object recognition | + | |
| - | systems. We developed the [[http://www.ros.org/ | + | |
| - | More information can be found on the RoboEarth project homepage. | ||
| - | [[http:// | ||
| - | ==== Acknowledgements ==== | + | Partners: |
| - | This project has received funding from the European Union Seventh Framework Programme FP7/ | ||
| - | === Publications === | ||
| + | This project has received funding from the European Union Seventh Framework Programme FP7/ | ||
Prof. Dr. hc. Michael Beetz PhD
Head of Institute
Contact via
Andrea Cowley
assistant to Prof. Beetz
ai-office@cs.uni-bremen.de
Discover our VRB for innovative and interactive research

Memberships and associations: