Differences
This shows you the differences between two versions of the page.
| Both sides previous revisionPrevious revisionNext revision | Previous revisionNext revisionBoth sides next revision | ||
| research:cram [2014/02/22 21:16] – tenorth | research:cram [2023/09/18 13:10] – [CPL Extension Modules] cstoess | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| ====== CRAM====== | ====== CRAM====== | ||
| //Cognitive Robot Abstract Machine// | //Cognitive Robot Abstract Machine// | ||
| + | ~~NOTOC~~ | ||
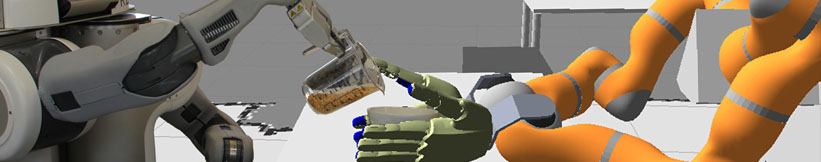
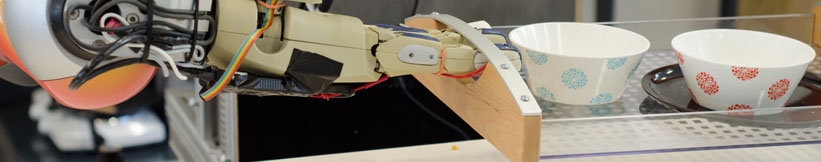
| CRAM (Cognitive Robot Abstract Machine) is a software toolbox for the design, the implementation, | CRAM (Cognitive Robot Abstract Machine) is a software toolbox for the design, the implementation, | ||
| - | everyday manipulation activities. CRAM equips autonomous robots with lightweight reasoning mechanisms that can infer control decisions rather than requiring the decisions to be preprogrammed. This way CRAM-programmed autonomous robots are much more flexible, reliable, | + | everyday manipulation activities. CRAM equips autonomous robots with lightweight reasoning mechanisms that can infer control decisions rather than requiring the decisions to be pre-programmed. This way CRAM-programmed autonomous robots are much more flexible, reliable, and general than control programs that lack such cognitive capabilities. CRAM does not require the whole domain to be stated explicitly in an abstract knowledge base. Rather, it grounds symbolic expressions in the knowledge representation into the perception and |
| - | and general than control programs that lack such cognitive capabilities. CRAM does not require the whole domain to be stated explicitly in an abstract knowledge base. Rather, it grounds symbolic expressions in the knowledge representation into the perception and | + | |
| actuation routines and into the essential data structures of the control programs. | actuation routines and into the essential data structures of the control programs. | ||
| {{ : | {{ : | ||
| - | The CRAM kernel consists of the CPL plan language and the KnowRob knowledge processing system. Both are tightly coupled to the perception and actuation components. CRAM is realized in | + | The CRAM kernel consists of the CPL plan language and the KnowRob knowledge processing system. Both are tightly coupled to the perception and actuation components. CRAM is realized in a highly modular way and can be extended with plug-ins providing additional cognitive capabilities. |
| - | a highly modular way and can be extended with plug-ins providing additional cognitive capabilities. | + | |
| ==== CPL Extension Modules ==== | ==== CPL Extension Modules ==== | ||
| - | * Designators are symbolic descriptions of entities such as objects (e.g. mugs, plates, ...), locations and parameterizations of actions. Designators unify symbolic and grounded concepts of the high level control program and the parameterization of the lower level components, which is necessary to efficiently reason about the execution of plans. | + | * Designators are symbolic descriptions of entities such as objects (e.g. mugs, plates, ...), locations, and parameterizations of actions. Designators unify symbolic and grounded concepts of the high level control program and the parameterization of the lower level components, which is necessary to efficiently reason about the execution of plans. |
| - | * Process Modules encapsulate lower-level control processes that can be activated, deactivated and parameterized by the high-level control program. They resolve symbolic properties of designators and generate the parameterization of the low-level control routines, by taking into account the current belief state. | + | * Process Modules encapsulate lower-level control processes that can be activated, deactivated, and parameterized by the high-level control program. They resolve symbolic properties of designators and generate the parameterization of the low-level control routines by taking into account the current belief state. |
| - | * Recording of an extensive | + | * Recording of an extensive |
| * Reasoning components include a bridge between CPL and KnowRob by incorporating the foreign language interface of SWI-Prolog into Common Lisp, a reasoning component based on the RETE algorithm and a library of predicates that allow for reasoning about plan execution, based on the execution trace. | * Reasoning components include a bridge between CPL and KnowRob by incorporating the foreign language interface of SWI-Prolog into Common Lisp, a reasoning component based on the RETE algorithm and a library of predicates that allow for reasoning about plan execution, based on the execution trace. | ||
Prof. Dr. hc. Michael Beetz PhD
Head of Institute
Contact via
Andrea Cowley
assistant to Prof. Beetz
ai-office@cs.uni-bremen.de
Discover our VRB for innovative and interactive research

Memberships and associations: